|
Wire and cable industry heavily depends upon
PVC for jacketing applications due to economic reasons. PVC is more
economical and more versatile as compared to PE - at least in power
cable system, which incidentally has almost 2/3rd share of the wire
& cable business. However, PVC, due to modest electrical properties
as compared to PE, has been gradually losing market share to PE
over the last two decades. PVC insulation not only has inferior
electrical properties, but has chances of higher electrical failure
at lower temperatures when compared to PE. Therefore, it is no wonder
that PE has taken over from PVC in the high tension power cable.
PVC, on account of its polarity, also does not have resistance to
high frequency electrical current that is required in telecommunication
cables. One of the major reason for a shift from PVC to PE is the
environmental disposal of PVC, which contains heavy metal as a heat
stabilizer. The shift is more in Europe and is also taking place
in North America. Asia, however, is slow in shifting to PE and still
predominantly uses PVC.
The wire & cable market can be basically classified into the
following:
 Power wires and cables:
Power wires and cables:
 |
Power transport and distribution networks Dry-insulated, armoured
or unarmoured cables:
# High and very high voltage,
# Medium voltage. |
 |
Low-voltage cables, aerial or underground for distribution networks
and connection. |
 |
Domestic wires and cables and appliance cords for mobile apparatus
with a 750 V maximum rated voltage. |
 |
Industrial cables, (maximum rated voltage 1000 V) for industrial
equipment and power supply of mobile apparatus. |
 Special cables and wires for intended purpose:
Special cables and wires for intended purpose:
 |
Wires and cables intended for electrical equipment fitted in automobiles,
aircrafts, lifts, ships, machine tools, railway materials, mines,
handlings, petrochemical industry, oil equipments, iron and steel
industry, welding, etc. |
 |
Precision and data cables for computer equipments, electronics
and automatic control instruments. |
 |
Heating cables. |
 Telecommunication wires and cables:
Telecommunication wires and cables:
 |
Cables for aerial and underground medium and long distance lines. |
 |
Cables for exchange area networks underground and aerial junctions,
subscribers cables. |
 |
Telephone cords. |
 |
Cables for private installations. |
 Submarine and underwater cables:
Submarine and underwater cables:
 |
Cables for power transport. |
 |
Cables for telecommunication. |
 Connection accessories for power cables:
Connection accessories for power cables:
 |
Low-voltage: connections, branching. |
 |
Medium voltage terminations. |
 |
Medium voltage plug-in terminations: separable connectors, bushings. |
 |
Medium voltage connections and branching for dry or paper insulated
cable, lapped, injected. |
 |
Prefabricated medium voltage connections for dry-insulated cable. |
 |
High and very high voltage: terminations, connections. |
Market shares are roughly estimated at:
 |
65% for power cables (50% for low-voltage and 15% for medium and
high-voltage) |
 |
25% for telecommunications |
 |
10% for other cables |
 Polymer properties:
Polymer properties:
Polymer properties essentially required for cables are:
All the layers of a cable covering are not insulating but some of
them are semiconductive or conductive to create EMI shielding. The
following figure shows some required properties for the used polymers.
Some of them deserve certain details:
 |
Electrical properties: apart from resistivity
or conductivity, the dielectric rigidity; for example, is important
to avoid the risks of breakdown and the dielectric constant |
 |
Mechanical properties: generally, flexibility
is required with fair mechanical performances.
For outside covering layer specific characteristics can be specified
such as high mechanical performances, light and/or ozone resistance
for outdoor or industrial applications, abrasion and tear resistances
for industrial applications. |
 |
Durability: Long-term ageing is nearly always
required and there are often other requirements for the covering
layer concerning UV or ozone ageing, moisture or water immersion
for submarine cables, and oil resistance for industrial applications. |
 |
Fire behaviour: ignition, smokes (opacity, toxicity
and corrosivity). |
 |
Cost: adapted to the applications. |
Figure 1 shows the principle of low-voltage wires and two examples
of cables.
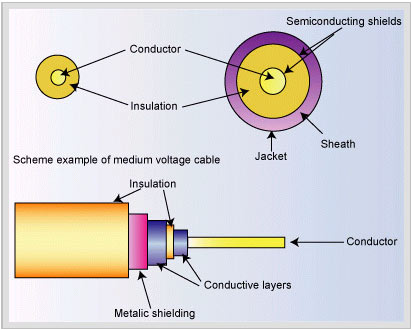
Figure 1: Principle of low-voltage wires and cables |
Figure 2 shows the principle of cable ribbon and bundle.
| Polymer |
Dielectric constant |
| Foam Polyethylene |
1.6
|
| Fluoropolymers |
2.0
|
| Polypropylene |
2.1
|
| Polyethylene |
2.3
|
| Butyl rubber |
2.3
|
| SBR |
2.9
|
| Polyamide |
3.0
|
| Silicone Rubber |
3.2
|
| PVC |
4.0
|
| Neoprene |
5.0
|
As shown in the following figure, PE is the most consumed polymer
(near 60%) under thermoplastic and thermoset (PEX) states, and also
foamed PE (2%). PVC is the second (roughly 30%) and the others are
rubbers, PP, TPEs, Polyamide, Polyurethane, Silicone, fluoropolymers.
| Total consumption share inthe Wires &
Cables sector |
| Polymer |
%
|
| LDPE |
5
|
| HDPE |
2
|
| LLDPE |
2
|
| PA |
2
|
| PVC |
8
|
Apart from PVC, PE and its copolymers, other polymers are used
for special applications justifying their higher cost. They are:
 |
Rubbers. |
 |
Fluoropolymers for high temperature and/or chemical resistance. |
 |
TPEs: special grades are marketed, eventually crosslinked after
extrusion. |
 |
Special polyurethane elastomers for telephone wire insulation. |
 |
Silicone cables for outside projectors, street lighting, drying
ovens, convectors, electric heating. |
|